The comparison between e-commerce and brick-and-mortar retail models has become increasingly significant as consumer behaviors evolve and technology continues to reshape the commercial landscape. This article delves into various aspects of each retail model, analyzing revenue potentials, cost structures, consumer behavior insights, market accessibility, inventory management, customer experience, technological integration, brand loyalty, and future growth prospects. By juxtaposing these elements, the article provides a comprehensive analysis of the strengths and weaknesses inherent in both paradigms, ultimately arguing for a hybrid, omnichannel approach that leverages the benefits of both to maximize profitability and growth.
Revenue Potential Analysis
The phenomenal revenue potential of e-commerce is a critical focal point. With global online sales projected to surpass $6 trillion by 2024, e-commerce is riding a wave of exponential growth driven by consumer demand for convenience, variety, and personalized shopping experiences. Online platforms benefit considerably from lower transaction costs and access to a global customer base, which enhances revenue opportunities significantly. As advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning shape the online retail landscape, retailers can offer highly personalized experiences that significantly boost customer satisfaction and repeat purchases.
On the flip side, brick-and-mortar stores possess advantages that are not as easily replicated online. The ability to provide tangible shopping experiences and spur impulse purchases is a major draw for physical stores. Despite the pandemic and shifting consumer habits that have reduced foot traffic, brick-and-mortar stores continue to thrive by adopting advanced technological solutions. Augmented reality and in-store apps, for instance, are being utilized to create immersive shopping experiences that enhance customer engagement and foster brand loyalty. By blending these technologies with a physical presence, retail stores can offer a unique experience that e-commerce cannot fully emulate.
Cost Structure Comparison
Understanding the cost structures associated with each retail model is paramount for making informed business decisions. E-commerce primarily entails technology-related expenses such as website development, maintenance, digital marketing, cybersecurity, and scalable cloud infrastructure. In addition to these fixed costs, e-commerce operations involve significant variable expenses related to shipping and warehousing. Leveraging data analytics enables e-commerce businesses to optimize ad spending and personalize customer interactions, thereby reducing customer acquisition costs. Despite these efficiencies, the significant logistics costs and the constant need for innovations in digital space present ongoing financial challenges.
In contrast, brick-and-mortar stores incur substantial fixed costs linked to leasing or purchasing physical spaces, which can vary greatly based on the location. Additional expenditures include utilities, staff salaries, and inventory management. To remain visually appealing and competitive, physical stores often require periodic renovations, which further adds to operational costs. Although physical stores might offer more predictable costs compared to their online counterparts, they also face the challenge of adapting to evolving consumer behaviors and technology trends. Many such stores are turning to experiential retail environments to justify their higher costs.
Consumer Behavior Insights
Consumer behavior is rapidly transforming the retail landscape, with digital-savvy shoppers playing a pivotal role. The article highlights a significant trend: 81% of consumers research products online before making a purchase, signifying a clear shift towards digital exploration. Online reviews, social media influence, and personalized recommendations are critical factors influencing purchasing decisions. With 72.9% of e-commerce sales emanating from mobile devices, optimizing websites for mobile users is essential to capturing this growing market segment. Convenient access through multiple devices supports the trend towards instantaneous researching and purchasing behaviors.
Personalization remains a key driver in both arenas. In the e-commerce sector, 80% of shoppers are more inclined to buy from companies that offer personalized experiences. AI-driven analytics facilitate tailored recommendations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Brick-and-mortar stores are evolving similarly, employing smart mirrors and augmented reality to engage customers and bridge the gap between digital and physical shopping. These technologies create a seamless integration of online and in-store experiences that caters to the preferences of modern consumers who value the sensory engagement unique to physical retail alongside the convenience of e-commerce.
Market Accessibility
Market accessibility is a critical battleground for both e-commerce and brick-and-mortar retailers. E-commerce platforms provide unparalleled reach, tapping into a global market without geographical constraints. With over 2.14 billion people expected to purchase goods and services online by 2023, the potential audience for e-commerce is vast. Platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce empower retailers to swiftly launch online stores, eliminate the need for a physical presence, and significantly reduce overhead costs. Such platforms democratize entrepreneurship, allowing smaller players to compete in a global market with relatively low initial investments.
In contrast, brick-and-mortar stores are constrained by foot traffic and local customer bases. Despite this limitation, physical stores account for 87% of retail sales in the U.S. as of 2023, highlighting their continued relevance. Employing a hybrid model that merges online and offline presences is key to maximizing market penetration. Strategies such as click-and-collect and augmented reality-enhanced physical stores bridge the digital and physical divide, enriching customer experiences and driving sales. These approaches provide the best of both worlds, allowing consumers to research and purchase online while enjoying physical store benefits like instant product availability and experiential shopping.
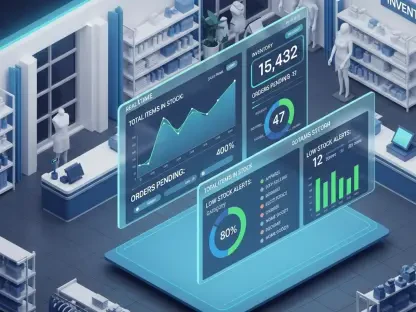
Inventory Management
The comparison between e-commerce and traditional brick-and-mortar retail models has gained increasing importance as consumer habits change and technology continues to transform the commercial landscape. This article explores the various dimensions of each retail model, focusing on revenue potentials, cost structures, consumer behavior trends, market reach, inventory management, customer experience, technological integration, brand loyalty, and future growth opportunities.
By examining these aspects, we gain a thorough understanding of the strengths and weaknesses inherent in both retail paradigms. E-commerce, for instance, often offers lower overhead costs and greater market accessibility, while brick-and-mortar stores may provide a more tangible shopping experience and foster personal connections with customers.
In an era where consumers seek convenience paired with tactile engagement, the article argues for a hybrid, omnichannel approach. This strategy combines the advantages of both e-commerce and physical stores, aiming to maximize profitability and foster sustainable growth. Ultimately, integrating both models’ benefits provides a more versatile and resilient retail strategy, essential for meeting the needs of today’s savvy consumers.